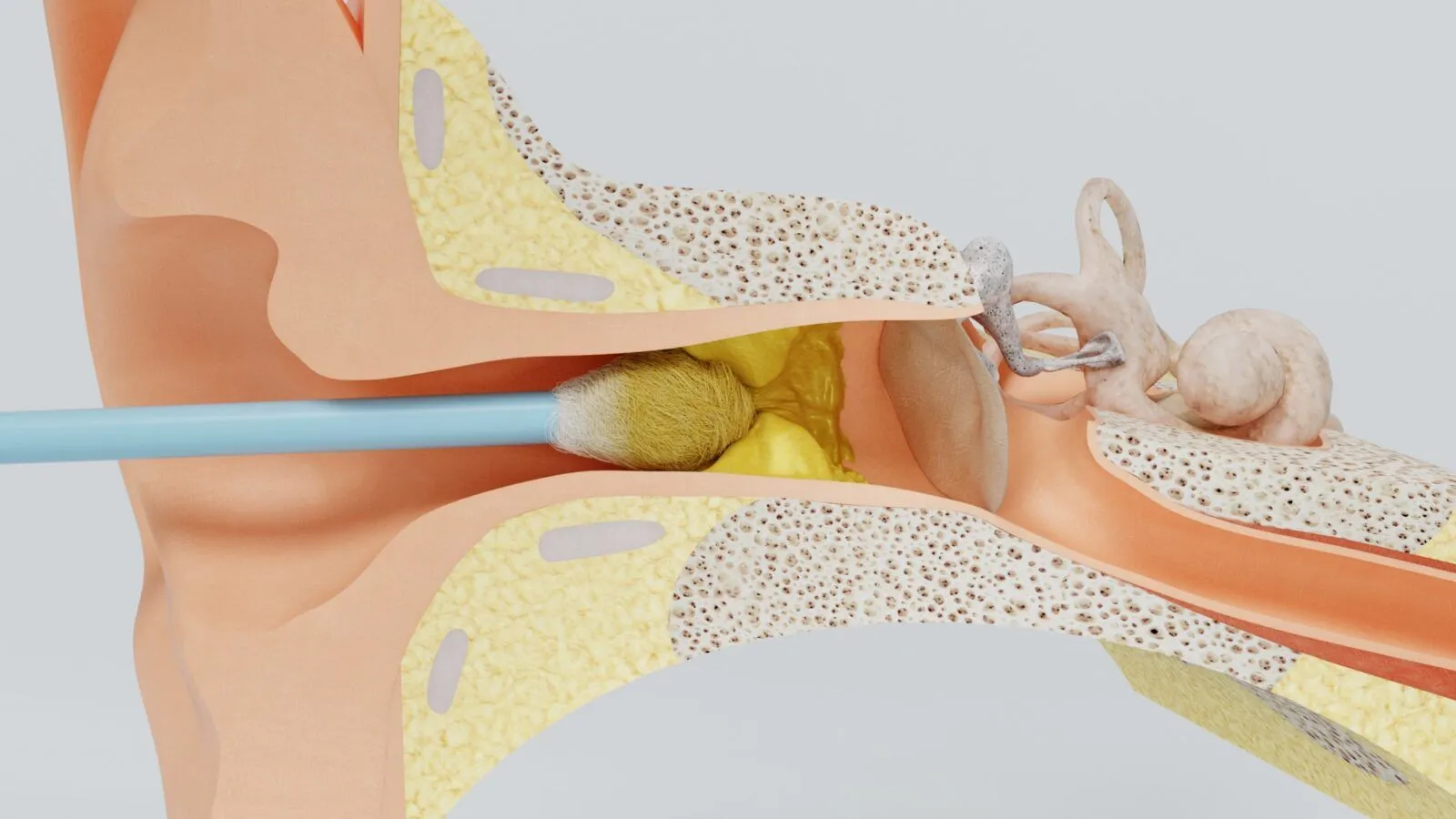
Earwax buildup is a common issue that quietly affects people of all ages, and this makes understanding its causes and simple management methods important for maintaining daily comfort without unnecessary worry.
Why does earwax form naturally?
Earwax forms as a natural protective substance inside the ear canal and develops from tiny glands that work continuously. This wax traps dust and microscopic debris. It also prevents bacteria from entering deeper areas. Many people do not realize that earwax has a vital purpose. The ear cleans itself slowly through natural movement. According to our editor’s research, some individuals produce more wax because their glands are more active. This is not dangerous but requires awareness. Understanding this natural process helps reduce unnecessary concerns.
What causes excessive earwax buildup?
Excessive wax buildup occurs when the natural cleaning process slows down. This happens for several reasons and often feels bothersome. Narrow ear canals can cause wax to accumulate quickly because there is less space for movement. Some people are simply more prone to this due to genetics. As a result of our editor’s reviews, stress and hormonal changes may also influence production. Using earbuds or cotton swabs pushes wax deeper. This is one of the most common causes mentioned by specialists. Applying heavy amounts of earphones during workouts also contributes to buildup.
How do habits affect wax production?
Daily habits can quietly increase wax formation. Wearing earplugs for long hours traps moisture inside the canal. This makes wax softer and more likely to gather. Cotton swabs create an illusion of cleaning while actually worsening the situation. According to our editor’s research, even hair sprays and powders can enter the outer ear and mix with wax. This makes it thicker. People who swim often may see changes because water alters the texture. Some start noticing itching as the wax becomes denser. These habits make maintenance more important.
Why do some people produce thicker wax?
Wax thickness varies from person to person. Genetics influence its color, texture, and density. Some produce dry flakes while others produce sticky wax. As a result of our editor’s reviews, people with skin conditions like eczema may create thicker wax because their skin sheds more. Climate also plays a role because dry environments may increase flakiness. Thick wax is not harmful but can block sound waves easily. This causes temporary hearing issues. Knowing your personal wax type helps in choosing proper management methods.
What symptoms indicate excessive buildup?
The most common symptom is a sensation of fullness. This feeling often comes and goes. Some people hear muffled sounds, which causes confusion. According to our editor’s research, light dizziness may also appear when wax presses against the eardrum. Itching is another frequent complaint that pushes people to clean their ears more aggressively. Sudden ringing sounds can occur in some cases. These symptoms are usually harmless but frustrating. Recognizing them early helps prevent deeper blockage.
How does earwax affect hearing clarity?
A blocked canal cannot transmit sound efficiently. This reduces clarity and sharpness. People sometimes describe conversations as distant. As a result of our editor’s reviews, hearing issues improve immediately once the blockage is removed. Many patients feel relieved after proper cleaning. The softness of wax also changes how much it affects sound. Hard wax blocks more strongly because it behaves like a physical barrier. When wax touches the eardrum, vibrations shift slightly. This causes temporary echo-like sensations.
What complications happen if buildup continues?
Long-term buildup can irritate the ear canal. Constant pressure may lead to inflammation. Scratching the area increases the risk of small injuries. According to our editor’s research, infections sometimes develop when bacteria become trapped behind the wax. Pain then becomes noticeable. Some patients report headaches linked to deep blockage. These complications are uncommon but possible. Acting early prevents them. Regular awareness reduces the chance of discomfort. Complications rarely become serious when managed correctly.
How can you safely manage earwax at home?
Safe at-home methods focus on softening the wax. Warm water rinsing during showers helps loosen buildup naturally. Tilting the head allows excess fluid to drain. As a result of our editor’s reviews, gentle softening drops can assist but must be used with care. Avoid inserting anything into the canal. Cotton swabs should be avoided completely because they push wax deeper. People with frequent buildup may use warm cloth compresses around the ear. This improves circulation and softens the wax. Simple habits protect the ear without causing harm.
When should professional removal be considered?
Professional removal becomes necessary when symptoms persist. Hearing difficulties that continue for days should be examined. According to our editor’s research, people who wear hearing aids need regular checks because wax interferes with the device. Specialists use safe tools that do not damage the canal. Patients often feel immediate relief. Hard or deep wax requires professional attention. A specialist can also detect hidden issues. Early professional care prevents further complications. Many people benefit from routine checkups.
Why is prevention easier than treatment?
Preventing buildup saves time and reduces discomfort. Avoiding cotton swabs is the first and most important step. Keeping ears dry prevents wax from becoming sticky. As a result of our editor’s reviews, limiting earbud use helps maintain airflow inside the canal. People with repeated buildup may use softening drops occasionally. Wearing ear protection in dusty environments also helps. Prevention relies on simple habits. These habits keep the ear’s natural cleaning mechanism functioning well. Over time, prevention becomes effortless.